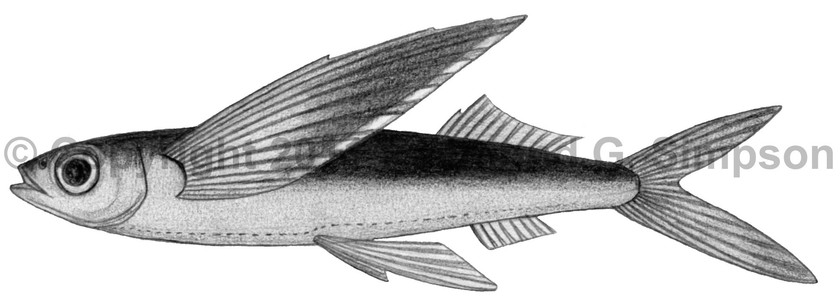
Common Name
Atlantic Flyingfish
Year Described
Valenciennes, 1847
Identification
Dorsal Fin: 11-14
Anal Fin: 7-11
Pectoral Fin: 14-18
Gill Rakers: 17-24 (first arch)
Predorsal Scales: 25-33 (usually 27-30)
Transverse Scale Rows: 6-8
Vertebrae: 45-47 (usually 46)
Body elongate with a rectangular cross-section. Head length 3.9-4.6 in SL. Jaw teeth conical; not conspicuous. Lower jaw slightly longer than upper. Palatine teeth absent. Pectoral fins long (1.4-1.6 in SL) with first ray unbranched, fin reaching to caudal fin base. Pelvic fins long (2.5-3.3 in SL), reaching well beyond anal fin origin, with pelvic origin nearer to anal fin than pectoral fin base. Dorsal fin relatively low (longest ray more than 10 times in SL). Origin of anal fin well behind that of dorsal fin (under 5-7th dorsal ray). Caudal fin forked with the lower lobe longer than upper. Lateral line low on side. Pectoral branch of lateral line absent. Juveniles with very short barbels (lost at 8-10cm SL) and expanded pelvic fins.
Color
Dark blue above, abruptly paler below. Pectoral fin gray, with indistinct paler crossband and a thin, pale posterior margin. Dorsal fin gray. Anal fin transparent. Pelvic fin transparent. Caudal fin gray. Juveniles with six body bands and dark blotches on fins.
Size
Maximum size to 27cm SL.
Habitat
Pelagic in neritic waters. Zooplanktivorous with demersal eggs.
Range
Continental: off the U.S. east coast to the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the southwestern Atlantic. Offshore only in the Gulf Stream and around Bermuda.
References
Parin, N.V. 2002. Exocoetidae (pp 1116-1134). In: Carpenter. 2002. The living marine resources of the Western Central Atlantic. Vol. 2: Bony fishes part 1 (Acipenseridae-Grammatidae). FAO Species Identification Guides for Fisheries Purposes. American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists Special Publication No. 5.