Common Name
Brazilian Clingfish
Year Described
Briggs, 1955
Identification
Dorsal Fin: 8-9 (rarely 7)
Anal Fin: 7-8
Pectoral Fin: 19-20
Caudal Fin: 11-12 segmented rays
Vertebrae: 30-32 total (13-14 precaudal, 17-19 caudal)
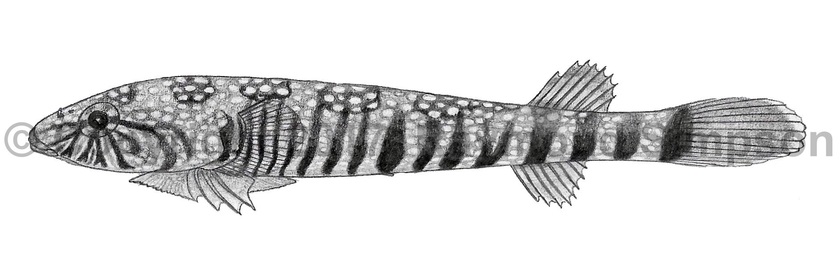
Body elongate and not greatly expanded on the head (typical for Tomicodon). Head about as wide as trunk. Eyes small. Mouth small. Teeth in single rows. Upper jaw with 3-6 canines and 8-10 incisors. Lower jaw with 3-6 canines and 6 incisors. Nasal flap well developed (length equal to nostril opening). Dorsal and anal fins placed far back. Anus usually closer to anal fin origin than to disk. Tail rounded. Anterior margin of disk crenulate, with fleshy tabs. Disk anteriorly with 6-7 rows of papillae and posteriorly with 6-7 rows of papillae. Region C without papillae (typical for Tomicodon). Anal fin origin under dorsal fin ray 3 or 4.
Color
Body pale olive green to pale brown with numerous close set white spots (especially on the dorsum). Four "8" shaped brown or olive saddles between back of head and dorsal fin also have white spots both surrounding and inside them. Two additional saddles under dorsal fin and on caudal peduncle. Saddles are broken into several brown vertical bands, some of them doubled and some fused. These bands can be solid colored or speckled with white. Reticulate white and brown lines radiate from eye. Fins pale or with fine speckles. Can change pattern intensity based on substrate.
Size
Maximum size to 27mm SL.
Habitat
Shallow coastal waters and tidepools on rock substrates.
Range
Known from SE Brazil (Santa Catarina to Rio de Janeiro States).
References
Williams, J.T. & J.C. Tyler. 2003. Revision of the western Atlantic clingfishes of the genus Tomicodon (Gobiesocidae), with descriptions of five new species. Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 621: 1-26.