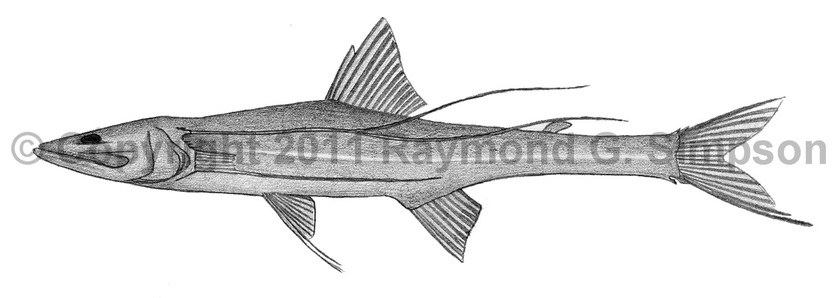
Common Name
Fourfinger Tripodfish
Year Described
Günther, 1878
Identification
Dorsal Fin: 12-15
Anal Fin: 8-9
Pelvic Fin: 9 (first two thickened and elongate)
Pectoral Fin: 2 tiny upper rays; then 2 elongate rays (joined for half of length); then 1 short and 2-3 tiny rays; then 7-9 long lower rays (with the lowermost one being much longer than the rest)
Branchiostegal Rays: 11-12
Gill Rakers: 11-12, 1 on corner, then 28-30 on lower limb (first arch)
Lateral Line: 57-63
Vertebrae: 54-59
Body fairly elongate with a tiny eye and a large mouth. Teeth small. Pectoral fins complex, with several elongate upper and a single lower ray extending beyond anal fin. Ventral fins with first two rays thickened and elongate (less than SL). Anal fin origin above last ray of dorsal fin. Lowermost two caudal fin principle rays are elongate (less than SL). Sub-caudal notch present. Adipose fin present. Body scales small, with tooth-like projections on scales behind pectoral fin base.
Color
Body black with paler scale pocket margins. Dorsal and caudal fins dark basally and light distally.
Size
Maximum size to 180mm SL.
Habitat
Continental shelf and slope from 462-1,408m over soft bottoms.
Range
North Carolina to SE Brazil, including the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea.
References
Franco, M.A., A.C. Braga, G.W. Nunan, & P.A. Costa. 2009. Fishes of the family Ipnopidae (Teleostei: Aulopiformes) collected on the Brazilian continental slope between 11 degrees and 23 degrees S. J. Fish Biol. 75(4): 797-815.
McEachran, J.D. & J.D. Fechhelm. 1998. Fishes of the Gulf of Mexico. Volume 1: Myxiniformes to Gasterosteiformes. University of Texas Press, Austin. i-viii + 1-1112.